Qml Weather
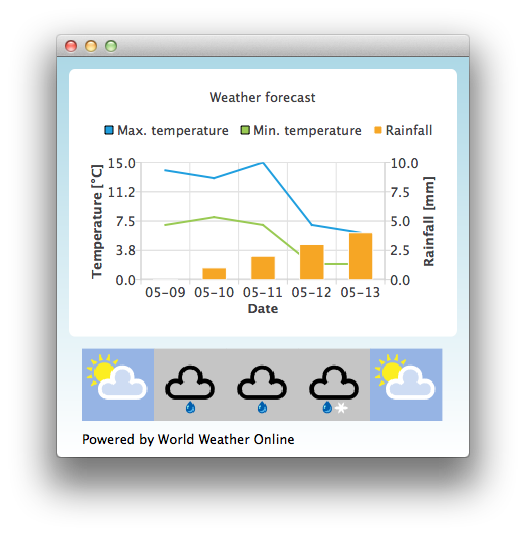
By default the application uses static test data to mimic a weather forecast. You can also obtain an application id from http://www.worldweatheronline.com/ to get access to weather API provided by World Weather Online. You can then give your application id as a parameter to the Qml Weather executable to make it use live data.
For example:
bin\qmlweather.exe 1234567890abcdef123456
The example application uses a ChartView and a some series to visualize weather data:
ChartView { id: chartView title: "Weather forecast" BarCategoryAxis { id: barCategoriesAxis titleText: "Date" } ValueAxis{ id: valueAxisY2 min: 0 max: 10 titleText: "Rainfall [mm]" } ValueAxis { id: valueAxisX // Hide the value axis; it is only used to map the line series to bar categories axis visible: false min: 0 max: 5 } ValueAxis{ id: valueAxisY min: 0 max: 15 titleText: "Temperature [°C]" } LineSeries { id: maxTempSeries axisX: valueAxisX axisY: valueAxisY name: "Max. temperature" } LineSeries { id: minTempSeries axisX: valueAxisX axisY: valueAxisY name: "Min. temperature" } BarSeries { id: myBarSeries axisX: barCategoriesAxis axisYRight: valueAxisY2 BarSet { id: rainfallSet label: "Rainfall" } }
To get data with weather forecast data, we make an HTTP GET request to World Weather Online. We request the response in JSON data format.
// Make HTTP GET request and parse the result var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest; xhr.open("GET", "http://free.worldweatheronline.com/feed/weather.ashx?q=Jyv%c3%a4skyl%c3%a4,Finland&format=json&num_of_days=5&key=" + weatherAppKey); xhr.onreadystatechange = function() { if (xhr.readyState == XMLHttpRequest.DONE) { var a = JSON.parse(xhr.responseText); parseWeatherData(a); } } xhr.send();
The JSON response contains an array of forecast data:
// Loop through the parsed JSON for (var i in weatherData.data.weather) { var weatherObj = weatherData.data.weather[i];
That is then used as input data for our series and a ListModel we use as a container for weather icon URLs:
// Store temperature values, rainfall and weather icon. // The temperature values begin from 0.5 instead of 0.0 to make the start from the // middle of the rainfall bars. This makes the temperature lines visually better // synchronized with the rainfall bars. maxTempSeries.append(Number(i) + 0.5, weatherObj.tempMaxC); minTempSeries.append(Number(i) + 0.5, weatherObj.tempMinC); rainfallSet.append(i, weatherObj.precipMM); weatherImageModel.append({"imageSource":weatherObj.weatherIconUrl[0].value});
Files: