Contents
Previous Next
Adding a Parallel Port in a Virtual Machine
If the virtual machine is configured with a parallel port, most guest operating systems automatically detect it at installation time and install the required drivers. Some operating systems, including Linux, Windows NT and Windows 2000, automatically detect the ports at boot time. Others, like Windows 95 and Windows 98, do not.
To add a parallel port to the virtual machine's configuration, complete the following steps with the virtual machine powered off. You can add the device from the console or from the management interface.
Note: In a Windows 95 or Windows 98 guest, run the guest operating system's Add New Hardware Wizard (Start > Settings > Control Panel > Add New Hardware) after you add the port and let Windows detect the new device.
Adding a Parallel Port from the Console
1. Open the virtual machine settings editor. Choose VM > Settings.
2. Click Add to start the New Hardware Wizard.
3. Select Parallel Port, then click Next.
4. Make the appropriate selection to use a physical parallel port or connect the virtual parallel port to a file, then click Next.
5. If you selected Use physical parallel port on the host, choose the port from the Physical parallel port list.
If you selected Output file, enter the path and filename in the Output file field, or browse to the location of the file.
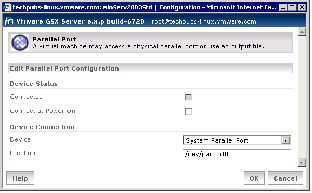
Under Device status, the default setting is Connect at power on. Clear the check box if you do not want the parallel port device to be connected when the virtual machine powers on.
6. Click Finish to install the virtual parallel port, then click OK to save the configuration and close the virtual machine settings editor.
Adding a Parallel Port from the Management Interface
1. On the Hardware page, click Add Device. The Add Device Wizard starts.
2. Click Parallel Port. The Parallel Port page appears.
3. To connect this virtual machine to the host's parallel port when the virtual machine is powered on, check Connect at Power On.
4. Specify whether to connect to the host's physical parallel port or to an output file. In the Device list, select System Parallel Port or Output File.
5. Enter the location of the device in the Location field. For example, the host's parallel port could be LPT1 or /dev/parport0.
Note: If you are connecting with a Windows console to add a physical parallel port to a virtual machine on a remote Linux host, be sure to specify a Linux device name here, such as /dev/parport0. If you are connecting with a Linux console to add a physical parallel port to a virtual machine on a remote Windows host, be sure to specify a Windows device name here, such as LPT1.
6. Click OK to add the parallel port.