Contents
Previous Next
Connecting Two Virtual Machines
You can set up the virtual serial ports in two virtual machines to connect to each other. This is useful, for example, if you want to use an application in one virtual machine to capture debugging information sent from the other virtual machine's serial port.
To install a direct serial connection between two virtual machines (a server and a client), take the following steps with the virtual machine powered off. You can add the device from the console or from the management interface.
Note: Make sure you performs these steps twice: once for the server virtual machine and once for the client virtual machine.
Connecting Two Virtual Machines from the Console
1. Connect to the server virtual machine with a console.
2. Open the virtual machine settings editor (VM > Settings).
3. Click Add to start the Add Hardware Wizard.
4. Select Serial Port, then click Next.
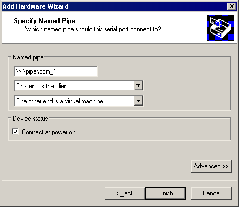
5. Select Output to named pipe, then click Next. The Specify Named Pipe screen appears.
6. Use the default pipe name, or enter another pipe name of your choice.
For a serial pipe on a GSX Server for Windows host, the pipe name must follow the form \\.\pipe\<namedpipe> — that is, it must begin with \\.\pipe\.
For a serial pipe on a GSX Server for Linux host, enter /tmp/<socket> or another Unix socket name of your choice.
Note: If you are using a Windows console to connect to a virtual machine on a remote Linux host, be sure to specify a Linux pipe name here, such as /tmp/<pipe>. If you are using a Linux console to connect to a virtual machine on a remote Windows host, be sure to specify a Windows pipe name here, such as \\.\pipe\<namedpipe>.
7. For the server virtual machine, select This end is the server.
For the client virtual machine, select This end is the client.
8. Select The other end is a virtual machine.
9. By default, the device status setting is Connect at power on. You may deselect this setting if you wish.
Click
Advanced if you want to configure this serial port to use polled mode. This option is of interest primarily to developers who are using debugging tools that communicate over a serial connection. For more information, see
Special Configuration Options for Advanced Users.
10. Click Finish, then click OK to save your configuration and close the virtual machine settings editor.
11. Repeat these steps for the client virtual machine.
Connecting Two Virtual Machines from the Management Interface
1. Connect to the server virtual machine with the management interface.
2. On the Hardware page, click Add Device. The Add Device Wizard starts.
3. Click Serial Port. The Serial Port page appears.
4. To connect this virtual machine to the device when the virtual machine is powered on, check Connect at Power On.
5. Connect to a named pipe on the host. In the Device list, select Named Pipe.
6. Enter the location of the file in the Location field.
For a serial pipe on a Windows host, the pipe name must follow the form \\.\pipe\<namedpipe> — that is, it must begin with \\.\pipe\.
For a serial pipe on a Linux host, enter /tmp/<socket> or another Unix socket name of your choice.
Note: If you are using a Windows console to connect to a virtual machine on a remote Linux host, be sure to specify a Linux pipe name here, such as /tmp/<pipe>. If you are using a Linux console to connect to a virtual machine on a remote Windows host, be sure to specify a Windows pipe name here, such as \\.\pipe\<namedpipe>.
7. For the server virtual machine, select This end is the server.
For the client virtual machine, select This end is the client.
8. Select The other end is a virtual machine.
9. Check
Yield CPU on Poll if you want to configure this device to use polled mode. This option is of interest primarily to developers who are using debugging tools that communicate over a serial connection. For more information, see
Special Configuration Options for Advanced Users.
10. Click OK to add the parallel port.
11. Repeat these steps for the client virtual machine.